Why the Thyroid Affects Weight and Skin
The thyroid gland is one of the most important organs in the body, directly influencing metabolism, energy levels, skin condition, and even mood. When it doesn’t function properly, it affects the entire body. That is why the topic of thyroid health has long been a key focus in the field of endocrinology, as its condition impacts not only a person’s weight but also appearance, particularly skin and hair health.
How the Thyroid Works
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of the neck. Despite its small size, it performs an enormous job — producing the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate metabolism, control the rate at which the body uses energy, processes fats and carbohydrates, and also control body temperature and heart function.
When the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), metabolism speeds up. A person may rapidly lose weight despite having a good appetite, experience excessive sweating, irritability, and a fast heartbeat. On the other hand, if the thyroid produces too few hormones (hypothyroidism), metabolism slows down. This leads to weight gain, fatigue, dry skin, and brittle hair.
Thyroid’s Influence on Weight
Weight is largely determined by the levels of thyroid hormones. These substances control how many calories the body burns at rest. With hypothyroidism, metabolism slows down, and even with the same diet, weight can increase. This happens because the body simply cannot process food as quickly as before.
Key Signs That Weight is Related to Thyroid Issues:
- Constant fatigue and drowsiness even after rest;
- Rapid weight gain without changes in diet;
- Swelling of the face and limbs;
- Feeling cold, slow reactions.
However, it’s important to understand that not every extra kilogram is related to thyroid problems. Sometimes, the cause is nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle. But if weight loss is impossible despite efforts, it’s worth checking hormone levels.
With hyperthyroidism, the situation is the opposite — a person quickly loses weight, sometimes to dangerous extremes. Metabolism is accelerated, muscles become depleted, and even with a strong appetite, weight loss continues. Such individuals often experience trembling hands, excessive sweating, and insomnia.
How the Thyroid Affects the Skin
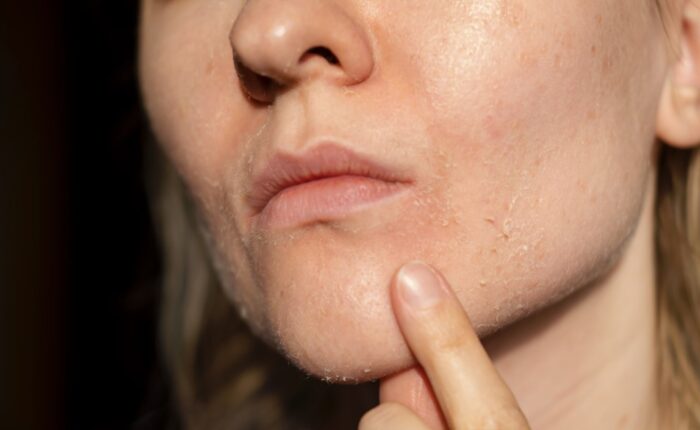
The skin is one of the first organs to react to thyroid imbalances. With hypothyroidism, the skin becomes dry, dull, and may develop flakiness and micro-cracks. This happens because thyroid hormones are involved in the skin cell renewal process. When they are insufficient, cell turnover slows down, and the skin loses its elasticity.
With hyperthyroidism, the skin may be excessively moist and hot, with frequent increased sweating. Due to the overactivity of sebaceous and sweat glands, the natural balance is disrupted, and the skin becomes sensitive and prone to irritation.
Typical Skin Symptoms of Thyroid Dysfunction:
- Excessive dryness and peeling of the skin;
- Brittle and falling hair;
- Weak nail growth, nail splitting;
- Increased sweating and oily skin (with hyperthyroidism);
- Swelling and paleness of the face.
These symptoms are often accompanied by other changes — decreased body temperature, fatigue, apathy, or, conversely, nervousness and increased anxiety.
Why It’s Important to Monitor Thyroid Health
The thyroid regulates the function of almost all body systems. If it is not functioning properly, not only weight and skin suffer, but also the heart, stomach, nervous system, and reproductive organs. A lack of hormones leads to a slowdown in body processes — metabolism, pulse, hair growth, and even thinking.
Main Causes of Thyroid Dysfunction:
- Insufficient iodine in the diet;
- Chronic stress and overwork;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Inflammatory processes and autoimmune diseases;
- Poor nutrition and vitamin deficiencies.
To maintain health, doctors recommend regularly checking hormone levels, especially if there are symptoms similar to metabolic disturbances or changes in the skin. It’s also important to monitor your diet — it should include enough iodine (seafood, seaweed, eggs, dairy products).
How to Support Thyroid Health
Supporting normal thyroid function isn’t that difficult if you follow simple recommendations.
Tips:
- Consume foods rich in iodine and selenium;
- Avoid chronic stress and overwork;
- Regularly consult with an endocrinologist;
- Monitor your weight and energy levels;
- Do not take supplements and medications without a doctor’s prescription.
In addition to nutrition, lifestyle plays a crucial role. The thyroid is sensitive to stress and lack of sleep, so it’s important to pay attention to rest. It’s also recommended to move more — physical activity helps maintain metabolism and improves overall health.
The thyroid is the body’s “motor”. How well it functions depends not only on weight but also on overall well-being, appearance, and mood. Disorders in its work can manifest in various ways — from weight fluctuations to changes in the skin and hair. Therefore, at any suspicion, it is important not to delay a visit to the doctor and undergo a thorough examination.