The Influence of Ergonomics on Industrial Product Design

In the realm of industrial product design, where form meets function, there exists a crucial yet often overlooked factor: ergonomics. Ergonomics, derived from the Greek words ergon (work) and nomoi (laws), is the science of designing products and environments to fit the people who use them. It encompasses a deep understanding of human physiology, psychology, and behavior, with the goal of optimizing performance, comfort, and safety.
The impact of ergonomics on industrial product design cannot be overstated. From the layout of a workstation to the shape of a handheld device, every aspect of a product’s design can either enhance or hinder its usability and user experience. In this article, we’ll explore the various ways in which ergonomics influences industrial product design and why it’s essential for designers to prioritize ergonomic principles.
1. Understanding User Needs
At the heart of ergonomics lies a profound understanding of human capabilities and limitations. Designers must consider factors such as anthropometry (the measurement of the human body), biomechanics, cognitive abilities, and sensory perception when creating products. By conducting user research and usability testing, designers can gain insights into how people interact with products in real-world scenarios. This understanding allows them to tailor the design to meet the specific needs and preferences of the target audience.
For example, when designing a computer mouse, ergonomists take into account the size and shape of the hand, the range of motion of the wrist, and the force required to click the buttons. By optimizing these factors, designers can create a mouse that fits comfortably in the hand and reduces the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
2. Improving Usability and Comfort
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in enhancing the usability and comfort of industrial products. A well-designed product should be intuitive to use and minimize physical and cognitive strain on the user. This involves factors such as control placement, button size and spacing, and feedback mechanisms.
For instance, in the design of a kitchen appliance such as a blender, ergonomics dictates that the controls should be conveniently located and easy to operate, even for users with limited dexterity or vision impairment. The handle should be ergonomically shaped to provide a secure grip and reduce hand fatigue during prolonged use. These small details can significantly improve the overall user experience and satisfaction with the product.
3. Ensuring Safety and Health
One of the primary goals of ergonomics is to prevent workplace injuries and promote user safety and health. Industrial products that are poorly designed can lead to musculoskeletal disorders, repetitive strain injuries, and other occupational health hazards. By applying ergonomic principles, designers can minimize these risks and create safer working environments.
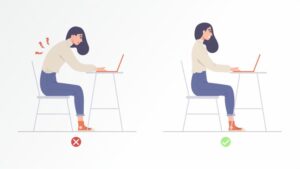
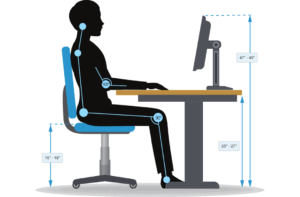
For example, in the design of office furniture such as chairs and desks, ergonomics dictates that the height, angle, and lumbar support should be adjustable to accommodate users of different heights and body types. Proper ergonomics reduces the risk of back pain, neck strain, and other musculoskeletal problems associated with prolonged sitting.
4. Enhancing Productivity and Performance

Ergonomics not only improves user comfort and safety but also enhances productivity and performance. By designing products that are well-suited to the capabilities and limitations of the human body, designers can help users perform tasks more efficiently and effectively.
For instance, in the design of power tools such as drills and saws, ergonomics dictates that the weight distribution should be balanced to reduce fatigue during extended use. The handles should be ergonomically shaped to provide a comfortable grip and maximum control. These design features enable users to work longer and more accurately, leading to increased productivity and quality of work.
In conclusion, ergonomics is a fundamental consideration in the design of industrial products. By understanding the needs and capabilities of users, designers can create products that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also comfortable, safe, and efficient to use. Whether it’s a smartphone, a car, or a piece of furniture, ergonomics influences every aspect of product design, ultimately shaping the way we interact with the world around us. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of ergonomics in industrial product design will only continue to grow, ensuring that products are not only innovative but also user-friendly and sustainable in the long term.